India Inflation remains a crucial factor influencing the Indian economy, shaping both monetary policies and business decisions. The Economic Survey 2024-25 highlights a moderating inflation trend, driven by global commodity price stabilization, policy interventions, and easing supply chain disruptions. However, food inflation remains a challenge, particularly for essentials like vegetables and pulses, due to climate-related supply shocks.
This blog provides a concise yet insightful overview of the key trends in inflation, price stability, and policy measures impacting businesses and consumers in India.
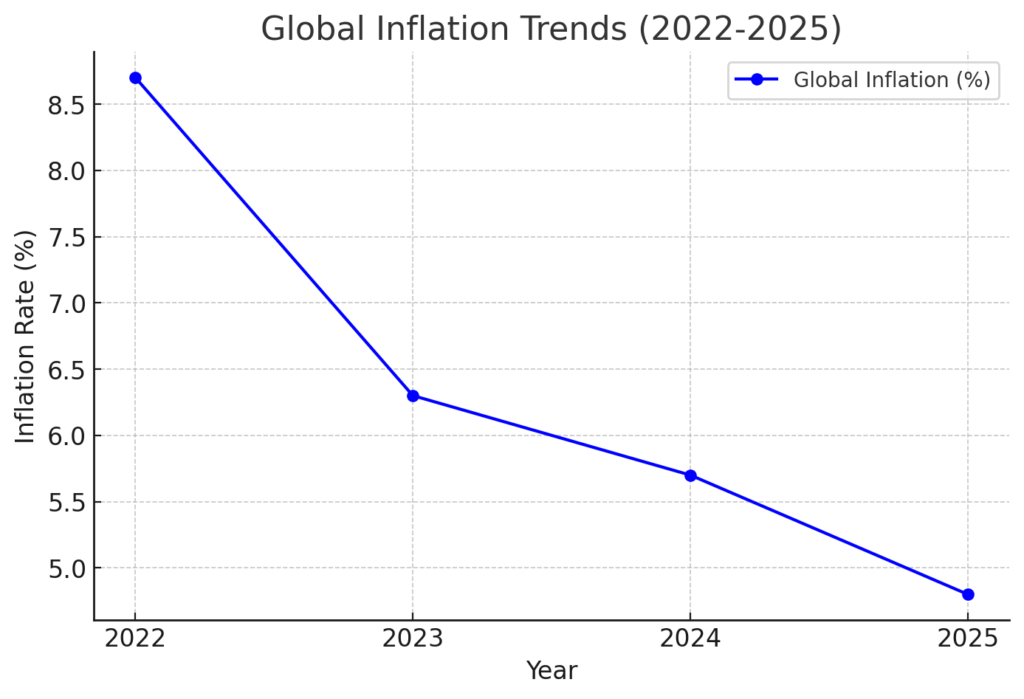
1. Global Inflation Trends: Easing Pressures but Continued Risks
- Global inflation peaked at 8.7% in 2022 due to supply chain disruptions and geopolitical conflicts.
- By 2024, global inflation moderated to 5.7%, reflecting policy effectiveness and improved supply conditions.
- Despite synchronized monetary tightening across countries, global output growth remained resilient.
Key Takeaways:
- Inflation is gradually aligning with policy targets, yet risks remain due to volatile commodity markets.
- Emerging economies, including India, must continue fiscal prudence and supply-side interventions.
2. India’s Inflation Trends: Softening Yet Volatile
- Retail inflation in India moderated from 5.4% (FY24) to 4.9% (FY25) (April-Dec).
- Core inflation (excluding food & fuel) reached its lowest in a decade, reflecting monetary policy effectiveness.
- Food inflation remains a key concern, driven by volatile vegetable and pulses prices.
Key Takeaways:
- Policy-driven inflation control is effective, but weather-driven food price volatility remains a risk.
- Businesses should anticipate fluctuating raw material costs, especially in food & agriculture-linked industries.
3. Food Inflation: Driven by Specific Commodities
- Vegetables & pulses accounted for 32.3% of total food inflation, despite having only an 8.4% weightage in CPI.
- Excluding pulses & vegetables, inflation drops to 3.2%, highlighting the disproportionate impact of a few items.
- Monsoon variability & supply chain disruptions impacted production and prices of onions, tomatoes, and pulses.
Key Takeaways:
- Vegetable & pulses inflation dominates price spikes, requiring targeted interventions.
- Climate-resilient agriculture and supply chain improvements are necessary for price stability.
4. Impact of Extreme Weather on Food Prices
- Frequent heatwaves & unseasonal rains significantly impact perishable crops like onions & tomatoes.
- Heatwaves in 2024 increased to 76 days compared to just 12 days in 2020.
- Crop damage area increased sharply, affecting supply stability & retail pricing.
Key Takeaways:
- Businesses in FMCG, retail, and food processing must hedge risks against climate-related price fluctuations.
- Investments in cold storage & supply chain efficiencies can mitigate short-term volatility.
5. Inflation Outlook & Policy Measures
- RBI projects retail inflation at 4.8% in FY25, gradually aligning with the 4% target by FY26.
- Global commodity prices expected to decline, reducing import-driven inflation.
- Key government measures to stabilize inflation:
- Stock limits & price control interventions for essential commodities.
- Encouraging climate-resilient crops to reduce weather-related food price volatility.
- Strengthening price monitoring systems for better supply-demand management.
Key Takeaways:
- Inflation is stabilizing, but businesses must stay cautious of food price volatility.
- Government & RBI measures will continue influencing inflation trends, requiring dynamic pricing strategies in key sectors.
Conclusion: Navigating Inflation Risks in 2024-25
The Economic Survey 2024-25 suggests that India is on track for inflation stabilization, but food inflation remains a key risk. Businesses, policymakers, and consumers must prepare for short-term volatility while focusing on long-term stability strategies such as supply chain improvements, climate-adaptive agriculture, and efficient fiscal policies.
LinkedIn Link : RMPS Profile
This article is only a knowledge-sharing initiative and is based on the Relevant Provisions as applicable and as per the information existing at the time of the preparation. In no event, RMPS & Co. or the Author or any other persons be liable for any direct and indirect result from this Article or any inadvertent omission of the provisions, update, etc if any.
Published on: February 1, 2025
