
India’s agriculture and allied sectors remain the foundation of the country’s economy, employing nearly 46% of the population and contributing 16% to GDP. Despite facing climate uncertainties, supply chain disruptions, and productivity challenges, the sector has demonstrated resilience with steady growth rates.
The Economic Survey 2024-25 highlights government initiatives, technological advancements, and policy reforms that have enhanced productivity, encouraged crop diversification, and improved farmers’ incomes. This blog explores key trends, opportunities, and challenges shaping the future of Indian agriculture and food management.
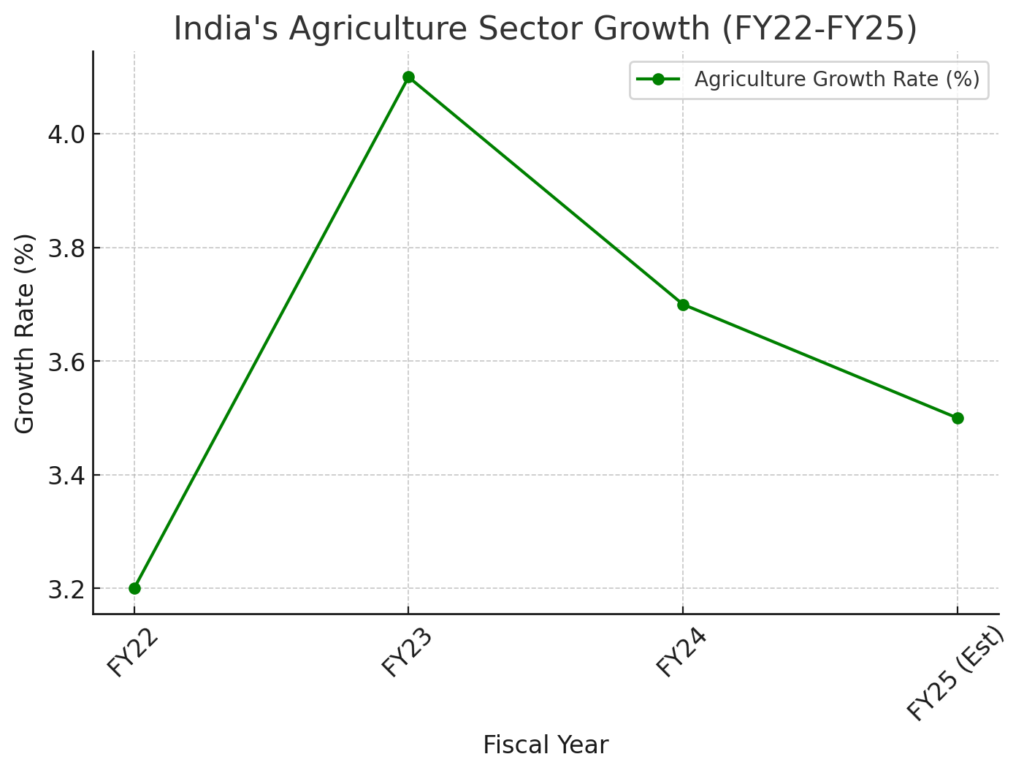
1. Agricultural Growth and Resilience
- India’s agriculture sector grew at 3.5% in Q2 FY25, reflecting a recovery from previous quarters.
- Average annual growth (FY17-FY23) stood at 5%, showcasing long-term resilience.
- Kharif foodgrain production for 2024 is projected at 1,647 Lakh Metric Tonnes (LMT), 89 LMT higher than last year.
Key Takeaways:
- Stable growth trends ensure food security and economic stability.
- Government support for remunerative pricing and credit access is boosting farmer confidence.
2. Crop Diversification and Productivity Enhancement
- India is the world’s second-largest cereal producer, contributing 11.6% to global output.
- However, crop yields in India are lower than those in other major agricultural economies.
- Horticulture, fisheries, and livestock sectors are witnessing higher growth rates than traditional farming.
Key Takeaways:
- High-value crops like fruits, vegetables, and pulses offer better profitability than cereals.
- Productivity-focused reforms are necessary to enhance India’s global competitiveness.
3. Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture
- Weather variability is a major risk, with 55% of India’s net sown area depending on rainfall.
- Drought-prone regions face 35% probability of drought occurrences, affecting crop output.
- Extreme rainfall events increased by 75% in Central India between 1950 and 2015.
Key Takeaways:
- Expanding irrigation coverage and investing in climate-resilient crops is crucial.
- Micro-irrigation and water conservation programs must be strengthened.
4. Role of Technology and Mechanization in Agriculture
Use of Smart Technologies for Higher Productivity
- 1,798 new high-yield seed varieties introduced to address climate resilience.
- Precision farming techniques (drones, AI, and IoT sensors) are gaining traction.
- Micro-irrigation has increased irrigation efficiency by 39-55%.
Key Takeaways:
- Technology-driven precision farming can significantly boost yields and resource efficiency.
- Farm mechanization and sustainable input usage should be prioritized.
5. Allied Sectors: Livestock, Fisheries, and Floriculture
Livestock: The Growth Engine of Indian Agriculture
- Livestock sector contributes 30% to total agricultural GVA, growing at 12.99% CAGR (FY15-FY23).
- Milk production alone is valued at ₹11.16 lakh crore, exceeding paddy and wheat combined.
Key Takeaways:
- Livestock and dairy are key drivers of income diversification for rural households.
- Investments in animal health, breeding programs, and digital livestock management will accelerate growth.
6. Agricultural Credit and Farmer Support Programs
- ₹25.48 lakh crore agricultural credit disbursed in FY24, up from ₹8.45 lakh crore in FY15.
- Kisan Credit Cards (KCC) issued to 7.75 crore farmers, with outstanding loans of ₹9.81 lakh crore.
- PM-KISAN scheme has benefited over 11 crore farmers with direct income support.
Key Takeaways:
- Access to affordable credit is driving investment in modern farming practices.
- Simplification of loan application processes through digital platforms can further boost farmer inclusion.
7. Food Security and Storage Infrastructure
- Under PMGKAY, 80 crore people receive free food grains, ensuring food security.
- Expansion of steel silos and smart warehouses to reduce post-harvest losses.
- e-NAM (National Agriculture Market) enables 1.78 crore farmers to access better pricing.
Key Takeaways:
- Strengthening food storage and logistics will enhance price stability and reduce wastage.
- Market reforms and direct-to-consumer platforms can increase farmers’ earnings.
8. Future Roadmap: Policy Reforms and Sustainability Initiatives
- Increase Agricultural Productivity: Promote high-yield seed varieties, R&D in biotechnology.
- Strengthen Irrigation & Water Management: Expand micro-irrigation and sustainable water use.
- Leverage Technology & Digital Platforms: Use AI, IoT, and blockchain for precision farming.
- Diversify Towards High-Value Crops: Expand horticulture, floriculture, and organic farming.
- Expand Rural Agri-Infrastructure: Build more warehouses, logistics hubs, and cold storage facilities.
- Encourage Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Strengthen corporate investments in farm technologies.
Conclusion
India’s agriculture and food management sector is at a transformational stage, with rising technology adoption, financial inclusion, and sustainability measures. While climate risks and productivity gaps remain key challenges, government policies, farmer-centric initiatives, and private sector involvement will play a crucial role in shaping the future of Indian agriculture.
With strong investments in innovation, sustainability, and market reforms, India is poised to strengthen its position as a global leader in food production and exports.
LinkedIn Link : RMPS Profile
This article is only a knowledge-sharing initiative and is based on the Relevant Provisions as applicable and as per the information existing at the time of the preparation. In no event, RMPS & Co. or the Author or any other persons be liable for any direct and indirect result from this Article or any inadvertent omission of the provisions, update, etc if any.
Published on: February 1, 2025
