
India’s economic growth is increasingly centered on inclusive development, with a strong focus on education, healthcare, skill development, and social welfare. The Economic Survey 2024-25 highlights the government’s commitment to ensuring equitable access to social services while leveraging technology and innovation to improve welfare delivery.
This blog provides insights into trends in social sector expenditure, education reforms, healthcare initiatives, rural development, and financial inclusion—all essential to achieving the goal of Viksit Bharat 2047.
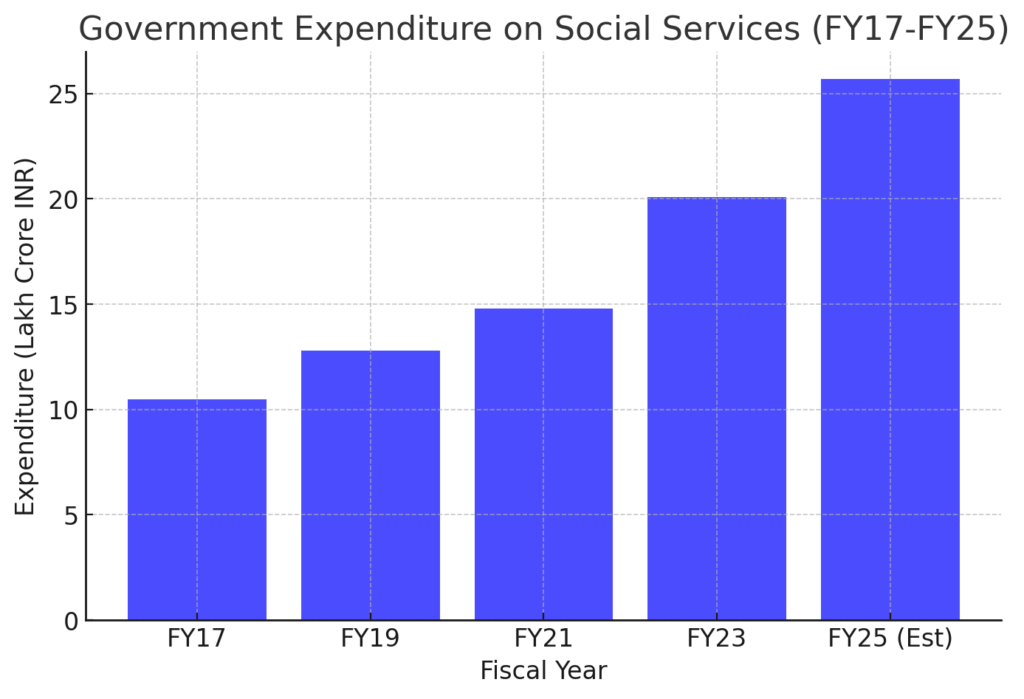
1. Social Sector Expenditure: A Growing Priority
- Government spending on social services increased from ₹14.8 lakh crore in FY21 to ₹25.7 lakh crore in FY25 (BE).
- Share of social sector expenditure in total government spending rose from 23.3% (FY21) to 26.2% (FY25).
- Key areas of spending: Education, healthcare, nutrition, rural development, and social security.
Key Takeaways:
- Rising social sector investment signals a commitment to inclusive development.
- Technology-driven welfare delivery is improving transparency and accountability.
2. Education: Strengthening Foundational Learning & Digital Literacy
Key Education Reforms Underway
- Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) reached near-universal levels at the primary level (93%).
- School dropout rates have declined, with secondary school retention at 63.8%.
- Government spending on education rose at a CAGR of 12% from ₹5.8 lakh crore (FY21) to ₹9.2 lakh crore (FY25).
Transforming Education Through Innovation
- NEP 2020 aims for 100% GER at the secondary level by 2030.
- NIPUN Bharat Mission focuses on foundational literacy and numeracy.
- Digital platforms (DIKSHA, SWAYAM, PM eVidya) expanding online learning access.
Key Takeaways:
- Ed-tech solutions are bridging learning gaps and boosting digital literacy.
- Peer learning and social-emotional education are enhancing student engagement.
3. Healthcare: Expanding Access and Strengthening Preventive Care
- Healthcare expenditure grew at 18% CAGR, from ₹3.2 lakh crore (FY21) to ₹6.1 lakh crore (FY25).
- PM Ayushman Bharat has provided ₹56,000 crore worth of cashless treatments to 5.9 crore families.
- Digital health initiatives (ABDM, telemedicine) are transforming healthcare access.
Key Takeaways:
- Preventive healthcare and digital transformation are key policy priorities.
- Ayushman Bharat is improving affordability and accessibility of healthcare.
4. Rural Development and Infrastructure Growth
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) has built 3.6 crore rural houses since inception.
- PM Gram Sadak Yojana added over 7.5 lakh km of rural roads.
- Jal Jeevan Mission has ensured piped water supply to 13 crore rural households.
Key Takeaways:
- Better infrastructure is improving quality of life and economic opportunities in rural areas.
- Government schemes are driving financial inclusion and self-reliance.
5. Household Consumption and Economic Empowerment
- Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2023-24 shows rural spending growth is catching up with urban areas.
- Gini coefficient improved, reflecting lower income inequality.
- Social welfare schemes (PMGKAY, DBTs, SHG loans) have boosted financial security.
Key Takeaways:
- Welfare policies are enhancing household consumption and reducing poverty.
- Direct Benefit Transfers (DBTs) and self-help groups (SHGs) are empowering women financially.
6. The Future of India’s Social Sector: Key Focus Areas
- Expand Digital & Skill-Based Education: Strengthen ed-tech platforms and vocational training.
- Enhance Universal Healthcare Coverage: Invest in telemedicine and digital health services.
- Accelerate Rural Development: Expand rural roads, housing, and water supply initiatives.
- Leverage Technology for Welfare Delivery: Strengthen real-time monitoring and direct transfers.
- Promote Financial Inclusion & Women’s Empowerment: Support SHGs and targeted cash transfer programs.
Conclusion
India’s social sector transformation is laying the foundation for inclusive economic growth. Education, healthcare, infrastructure, and financial inclusion initiatives are key pillars of welfare-driven development. With policy innovation, increased investments, and targeted interventions, India is moving toward a more equitable and empowered society.
LinkedIn Link : RMPS Profile
This article is only a knowledge-sharing initiative and is based on the Relevant Provisions as applicable and as per the information existing at the time of the preparation. In no event, RMPS & Co. or the Author or any other persons be liable for any direct and indirect result from this Article or any inadvertent omission of the provisions, update, etc if any.
Published on: February 1, 2025
